Motherboard:
A motherboard is the heart
of a computer. It is the main printed circuit board present in the computers
which holds the main electronic components of the system like the central
processing unit and memory and also provides the connectors for other important
peripherals. A motherboard is a large system in itself which contains a number
of subsystems like the processor and other components. The basic function for
which a motherboard is used in a computer is that it holds the important
electronic components of the system including the memory and central processing
unit and helps in establishing some sort of bridged connection between other
internal components of the system.
XT Motherboards:
XT Stands for eXtended
Technology. These are all old model motherboard. In this motherboards, we find
old model processor socket LIF (Low Insertion Force) sockets, ram slots Dimms
and ISA (Industry Standards Architecture) slots, 12pin Power Connector and no
ports.
They have slot type
processors, Dimms memory modules, ISA slots for add-on card, and no ports.
There are connectors and add-on cards for ports.
Eg: Pentium-I,
Pentium-MMX, Pentium -II and Pentium-II Processors.
AT Motherboard
·
An AT motherboard is a motherboard which
has dimensions of the order of some hundred millimeters, big enough to be
unable to fit in mini desktops. The dimensions of this motherboard make it
difficult for the new drives to get installed. The concept of six pin plugs and
sockets is used so as to work as the power connectors for this type of
motherboards.
·
The hard to distinguish power connector
sockets make it difficult for many users to easily make the proper connections
and thus leading to the damage of the device.
·
Produced in the mid 80’s, this
motherboard lasted a good span from the Pentium p5 to the times when Pentium 2
had been started to be used.
Baby AT Motherboards:
Baby AT Motherboards
have the combination of XT and AT. They have both slot type processor sockets
and PGA processor sockets, SD Ram slots and DDR Ram slots, PCI slots and ISA
slots, 12 Pin power connector and 20Pin power connector and Ports.
Eg: Pentium-III and
Pentium-IV
ATX Motherboards:
ATX stands for Advanced
Technology eXtended. latest motherboards all are called as ATX motherboards.
designed by ATX form factor. In this motherboards, we find MPGA Processor
Sockets, DDR Ram slots, PCI slots, AGP slots, Primary and secondary IDE
interfaces, SATA connectors, 20pin and 24 pin ATX power connector and Ports.
Eg: Pentium-IV, Dual
Core, Core 2 Duo, Quad Core, i3, i5 and i7 Processors.
Form Factor
When referring to computer hardware, a form factor is a specification of its layout and physical dimensions. Form factors help prevent incompatibilities between multiple hardware manufacturers.
The form factor of a motherboard determines the specifications for its general shape and size. It also specifies what type of case and power supply will be supported, the placement of mounting holes, and the physical layout and organization of the board. Form factor is especially important if you build your own computer systems and need to ensure that you purchase the correct case and components.
Desktop motherboards have standard form factors. The standard size and shape allow motherboards from different manufacturers to be interchangeable.
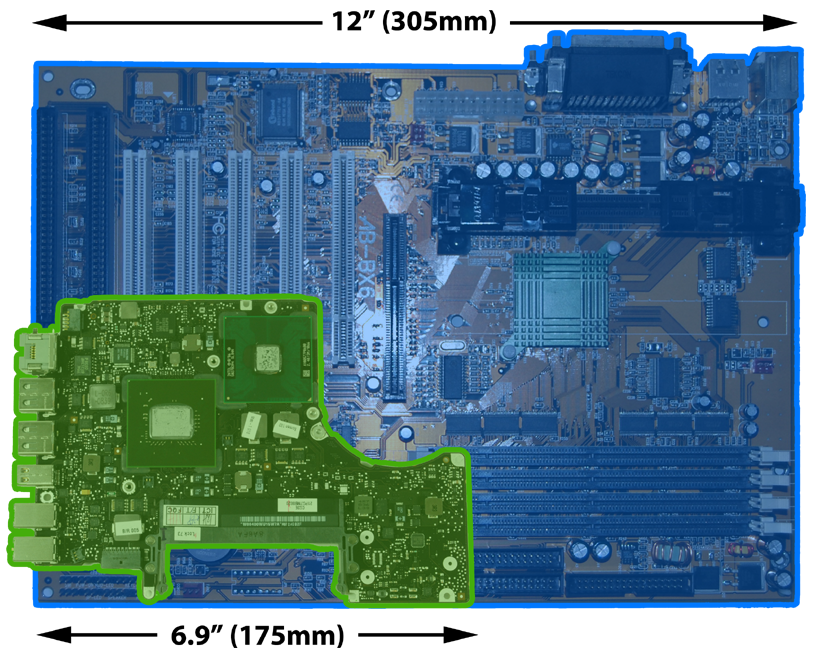
Laptop motherboards vary by manufacturer and are proprietary. When you repair a laptop, it is strongly recommended that you obtain a replacement motherboard from the manufacturer of the laptop. Figure 1 shows a desktop motherboard and a laptop motherboard.
Laptop motherboards and desktop motherboards are designed differently. Components designed for a laptop generally cannot be used in a desktop. It shows a few examples of the design differences.
Laptops, some printers, and routers have space restrictions; therefore, they use Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Modules (SODIMMs), as shown in Figure.





No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.